This post is also available in: polski (Polish)
Project of control and monitoring of the production process in a fermentation biogas plant
Introduction
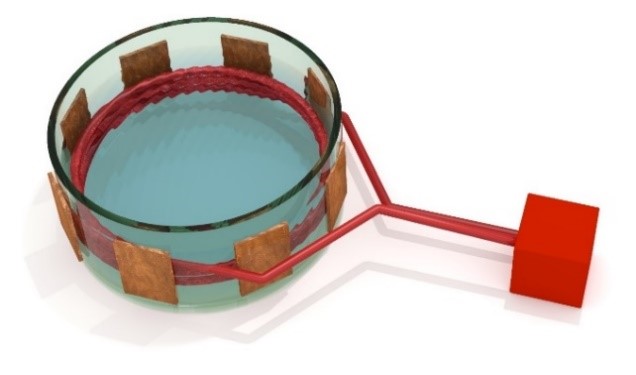
Fig.1. The heating installation diagram
Fermenter
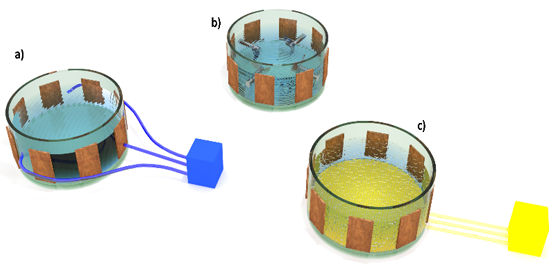
Mixing the contents of the fermenter facilitates degassing, allows to ensure a constant temperature and uniform growth of microorganisms in the entire volume of the fermentation chamber, as well as prevents the formation of a scum on the biomass surface. There are three main methods of mixing: mechanical, hydraulic and pneumatic. The most common is mixing with use of vertical, horizontal or diagonal mechanical agitators (fig. 2b). When capacitance tomography is used to study the contents of the fermenter, it is of limited usage due to the inhomogeneity introduced into the tested environment, which constitutes a significant difficulty in determining the condition of biomass. The second more useful method is hydraulic mixing, in which pumped biomass is used to mix the contents of the fermenter (fig. 2a). The last of the above-mentioned methods is pneumatic mixing (fig. 2c), which uses biogas pumped under pressure in the lower part of the fermentation reactor. Both, hydraulic and pneumatic mixing do not require installation of devices inside the fermenter, therefore do not introduce point disturbances to the studied object, which has a positive impact on the quality of tomographic measurements.
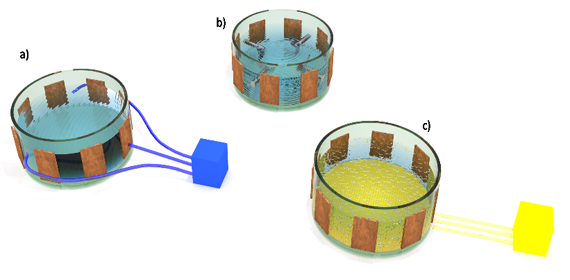
Fig. 2. Biomass mixing a) hydraulic, b) mechanical, c) pneumatic
Control system
The provision of raw materials may be carried out continuously or cyclically, every few hours. The amount of introduced substrates should result from the chemical composition (proportion C : N 100 :3), the hydraulic retention time of 20 to 60 days depending on the substrates which were used and the pollutant load in the chamber, which usually ranges from 3.5 to 6 kg oDM/m3/day.
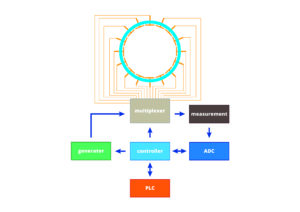

Capacitance tomography
Information about the distribution of the permeability coefficient is obtained by carrying out multiple measurements of the capacitance on the surface of the object with variable position of the excitation electrodes. The basic problem is to determine the dependance of permeability distribution with the known and defined internal structure of the tested element by means of experiments. The measured capacitances are in the order of femtofarads, which requires special measurement techniques. The measuring system consists of a sensor, specialized electronics for capacitance measurements and a reconstruction system. Currently, using a PC computer for the reconstruction is most convenient. Electric Capacitance Tomography enables the observation of physical and chemical phenomena without the need to penetrate their interior. The source of information are the electric capacitances between the electrodes placed around the measuring sensor. On the basis of the collected measurements of electric capacitance – by solving the inverse problem for the electric field, it is possible to obtain the image of the electric permittivity distribution inside the area of measuring sensor.
A very important feature of the measurement in the case of Electric Capacitance Tomography is the lack of the need for physical interaction of the sensor with the tested medium and owing to this, the method is non-invasive; it does not disturb the ongoing industrial process. Another advantage of this measurement technique is the fast pace of collecting measurement data. Verification of the obtained results will be carried out by comparing the simulation results with the results of analytical study for the set of test data. The measurable effect of the task will be a working simulation model, which will allow for further research on practical applications.
Summary
Using capacitance tomography to study the state of fermenting biomass should bring benefits in the form of a larger amount of information about the current state of fermentation process. This information, available on a continuous basis, can be used in the control systems of a biogas plant, and thus will contribute to increasing its efficiency. Unfortunately, due to the presented in the document problems related to implementing capacitance tomograph in existing and working biogas plant, what may turn out to be difficult and impossible to carry out, therefore it is necessary to look for such technological solutions that will make use of capacitance tomography possible in this area of economy. The implementation of capacitance tomograph should start at the stage of designing the biogas plant and the production process, but due to the significant costs of such an investment, appropriate tests on models or experimental installations should be carried out beforehand. The following works are expected to be carried out in several areas: examining the possibility of integration of industrial control systems with capacitance tomograph, tomographic examination of biomass at different stages of fermentation and examining the possibility of constructing a measuring probe adjusted in terms of its size and structure to industrial fermentation reactors.
The project is co-financed from the European Union funds.