This post is also available in: polski (Polish)
From 01/11/2015 Netrix SA has been implementing a project co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund entitled “Hybrid tomograph for testing the moisture and condition of buildings”.
Project description
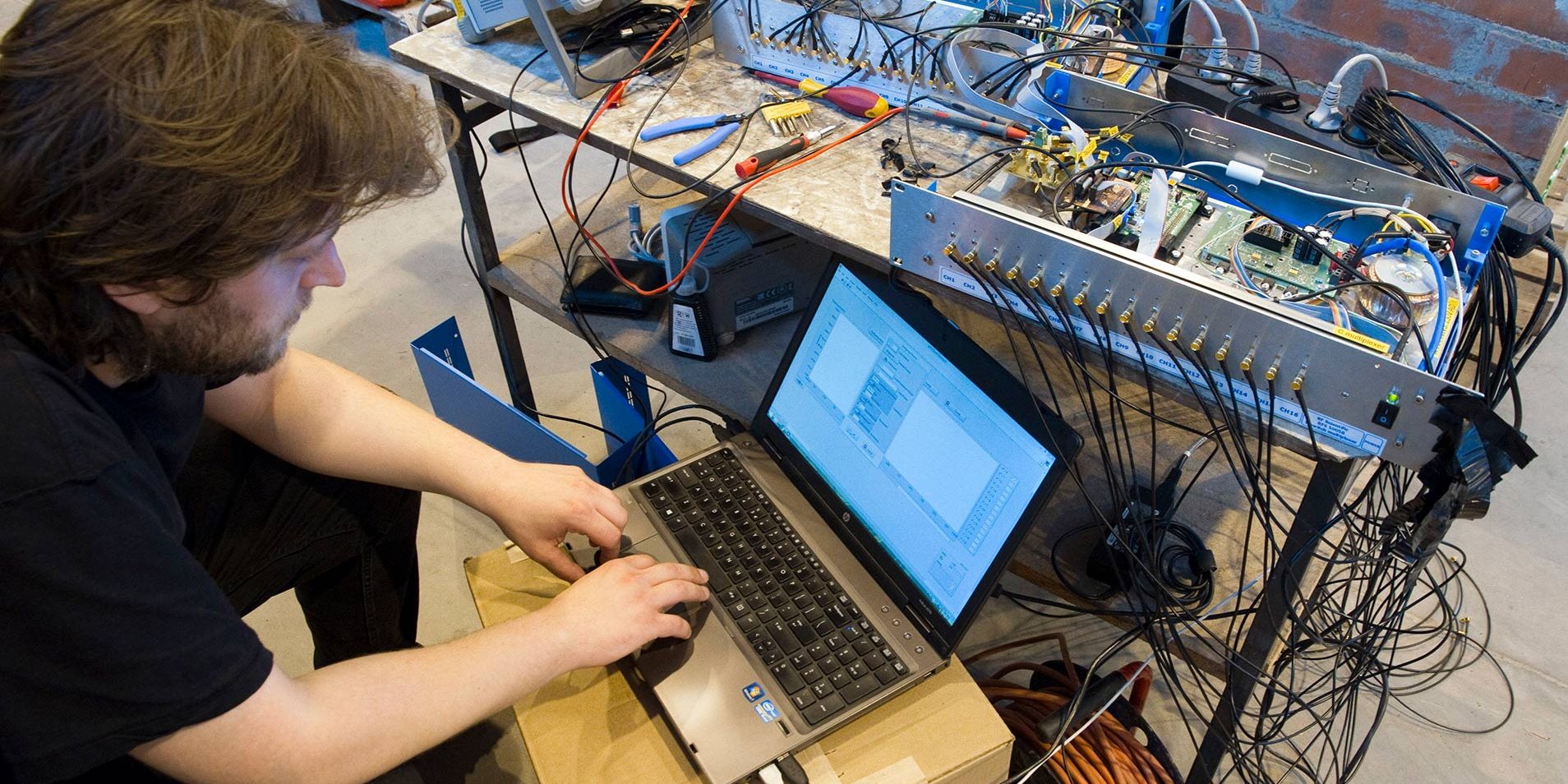
The project involves creating a tomographic system (measuring device and software for the interpretation of measurements results) using both impedance tomography and capacitance tomography for the spatial analysis of the degree of moisture in walls. In addition, due to applying two tomographic techniques, the prototype device will allow to analyze the condition of slabs, with particular reference to blocks of flats from the so-called large slab (tests of fastening and condition of reinforcement in concrete walls). The prototype of ECIT device (Electrical Capacitance and Impedance Tomograph) will allow simultaneous measurement of capacitance and impedance by means of active surface electrodes. The hybrid tomograph is a modular, compact, configurable device enabling work in various measurement systems.
The basic element of the system will be an active measuring electrode, containing analog keys, as well as ADC and CDC converters. The active electrodes are connected to a digital module reading and transmitting data to the control module. The control module will ensure configuration of the device, application of the measurement cycle, pre-processing of the measurement data and communication with the computer acquisition and visualization system.
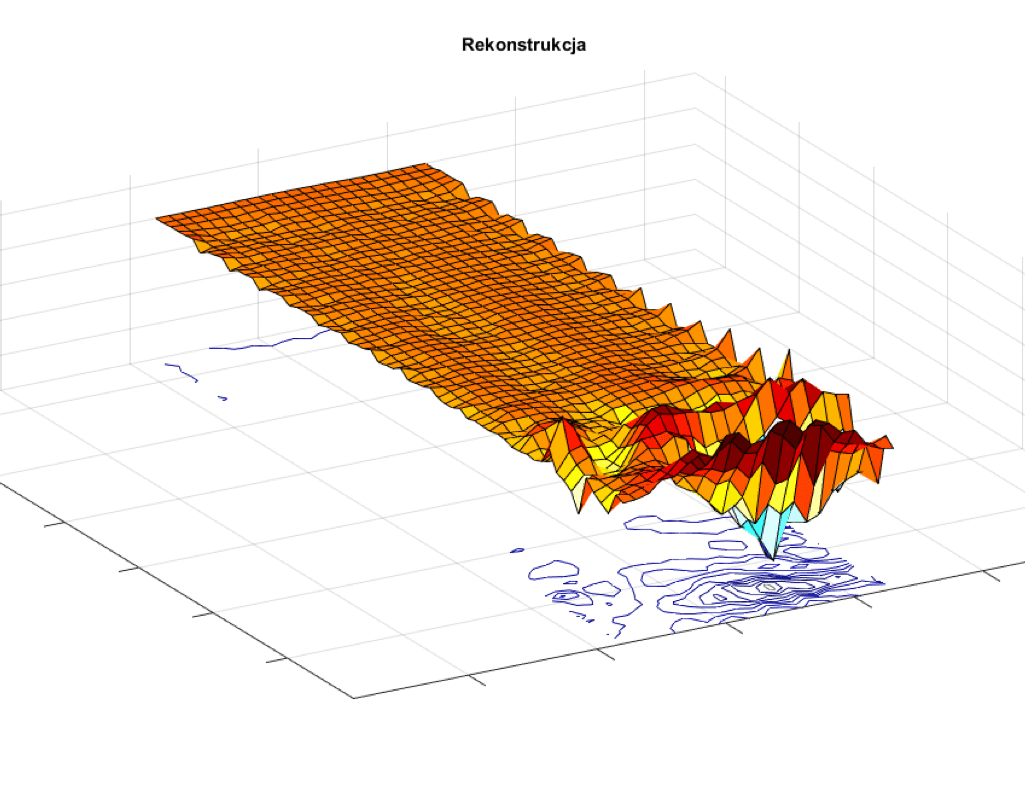
The tomograph will ultimately support a probe equipped with 32 active electrodes. The last part of the system is the image reconstruction software. The planned solution will be based on the latest scientific achievements in the field of image reconstruction.
The project will develop and apply new procedures and algorithms in the field of theoretical and numerical mathematics using the issues of neural networks, genetic algorithms, rough sets theory, topological methods, hybrid algorithms, fuzzy sets and gradient methods. The developed algorithms will develop methods and concepts related to reconstruction and analysis of images, as well as the appropriate form of their presentation.
The aim of the project
The aim of the project is to create a hybrid tomographic measuring system (measuring device and software for measurements results interpretation) using both impedance and capacitance tomography. The tomographic system, which will be created as the result of the described above project, will be an innovative and cutting-edge solution in detecting moisture and defining the condition of buildings, both in terms of the measuring device itself and implemented algorithms. The use of modern tomographic techniques as well as intelligent algorithms (e.g. neural networks) will allow for a non-invasive and very precise spacial determination of the moisture level. Electrical Tomography (ET) includes, under various names, many tomographic techniques depicting the electrical parameters of an object placed in the measurement space. In the case of Electrical Capacitance Tomography (ECT) it will be imaging of electric permittivity ε, and in the case of impedance tomography (EIT – Electrical Impedance Tomography) it is a technique of imaging the spatial distribution of conductivity σ. The aforementioned types of tomography generate an electric field as a result of a stimulation of current (EIT) or voltage (ECT).
Due to different operating principles (excitation), EIT tomography and ECT tomography have not been used so far for simultaneous permittivity and conductance imaging in one measuring probe.
Although there are many methods of examining the moisture content in brick walls, currently there is no one universal method which can be adopted in various measurement conditions. Each one of them has its advantages, disadvantages and conditions allowing it to be used only in certain circumstances. The main problem currently encountered in the study of wall dampness is lack of a method allowing to determine its spatial distribution without the need to collect samples.
The vast majority of available research methods only allow for a spot evaluation of moisture (gravimetric method), which only makes it possible to construct discrete models. In the case of using indirect methods (thermal imaging camera), it is possible to determine the concentration of water only on the surface of the wall or in its subsurface zone. This fact is a major problem in the case of thick walls, because the moisture inside the wall is usually a few percent higher than on its surface. The destructive nature of currently used methods requiring sample collection is unacceptable, especially in historical buildings. In such cases, only non-invasive methods can be used.
The proposed hybrid method, in which the assessment of the moisture content of building materials consists in an indirect determination of this value by defining another physical property (ε, σ), will allow the measurement to be carried out many times without any damage to the examined object. At the same time, the distribution of moisture inside the wall will be archived using a computer storage media and compared with the subsequent test results at any time. The method will be very useful for the control and effectiveness of protection against moisture, as well as the effectiveness of accelerated drying, especially in thick walls. Impedance tomography as well as capacitance tomography are relatively new imaging techniques and their development is dynamic. In recent years, they have been applied in various fields, ranging from the refining industry, through the electronics industry, to biomedical applications.
Process computed tomography may be applied in the following fields: medicine, eddy current testing, detection and control of laminar and turbulent fluid flows or in geophysics. The main advantages of the proposed hybrid tomographic systems are: non-invasive and non-destructive examination of a given object, the possibility of imaging small changes in both permittivity and conductivity, as well as low costs of the measuring device and its operation. The advantage of the proposed hybrid tomographic system also consists in the use of new innovative procedures and algorithms in the field of theoretical computer science and numerical mathematics. The implementation of proprietary algorithms to solve the problem of image reconstruction will improve the quality (resolution) of the received image. The final solution will test and apply algorithms using the issues of neural networks, genetic algorithms, fuzzy and approximate sets theory, topological methods and hybrid algorithms.
The value of the Project is 6,472,397.99 PLN
The contribution of European Funds amounts to 4 833 136.33 PLN